Recycling-based economy, innovation in battery technology using solar energy panels
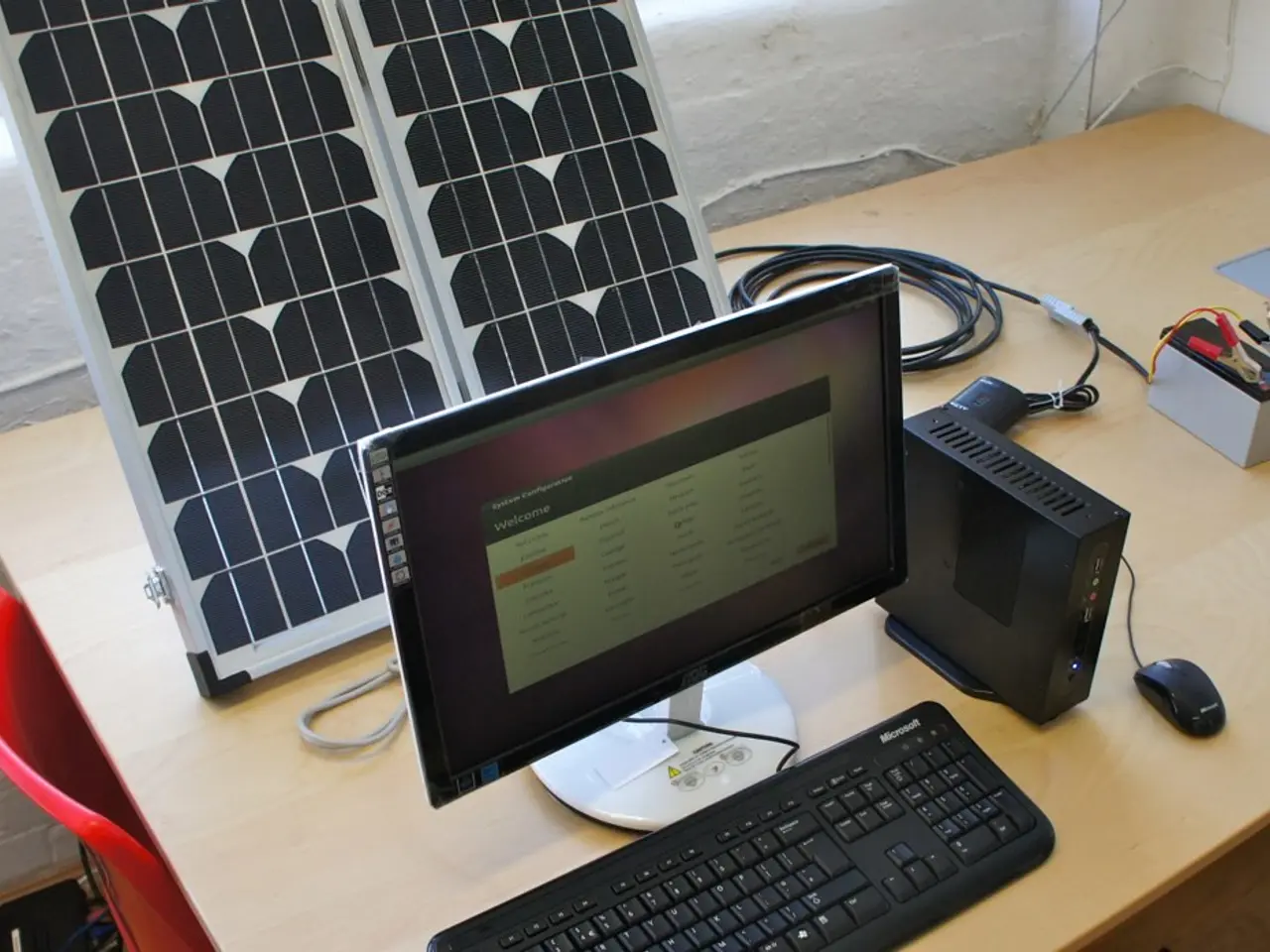
Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy, and Sustainable Economic Development (ENEA) is making strides in the field of renewable energy, particularly in the end-of-life sector of solar panels. ENEA researchers, led by Marco Tammaro, head of the Laboratory of Technologies for reuse, recycling, recovery, and valorization of waste and materials, have developed a groundbreaking recycling process.
The process is aimed at recycling end-of-life solar panels, a move that addresses the growing global photovoltaic waste. The recovery process uses an infrared treatment for thermal degradation of the plastic material layer, avoiding combustion and reducing atmospheric emissions. This method is beneficial for reducing atmospheric emissions and is part of ENEA's commitment to environmental sustainability.
The technology used for the transformation of silicon is not specified, but the process involves its transformation. The separated materials, including glass, cells, electrical contacts, and plastic components, are being used for other purposes, contributing to resource efficiency.
The goal of this research and innovation is to develop less expensive and more efficient batteries. The recovered silicon from end-of-life solar panels is being used to create innovative nanomaterial for such batteries, potentially revolutionising the energy storage sector.
ENEA researchers have filed two patents for these processes, marking significant steps in the field of solar panel recycling. However, the specific details of these patents, their influence on battery development, and the implications for waste management remain to be fully understood, as no concrete details were found in the provided search results.
The separation of materials is done using infrared technology, a choice that aligns with ENEA's focus on reducing problems related to resource scarcity and reducing imports from abroad. This recycling process is expected to be less expensive than primary raw materials, making it a promising solution for the future of sustainable energy.
While the exact impacts of these patents are yet to be fully realised, ENEA's work in solar panel recycling is a significant step towards a more sustainable, resource-efficient, and self-sufficient energy future. For detailed and accurate information on ENEA’s patents related to solar panel recycling, one may need to consult patent databases such as the European Patent Office or ENEA’s official publications directly.
- The science of recycling end-of-life solar panels is advanced by ENEA, particularly in the field of environmental science.
- The renewable-energy industry benefits from ENEA's research, as their newly developed recycling process addresses the growing photovoltaic waste problem.
- The finance sector may see positive impacts from ENEA's work, as the recycling process is expected to be less expensive than primary raw materials, potentially leading to cost-effective energy solutions.
- ENEA's technology for waste materials separation, using infrared technology, aligns with their commitment to resource efficiency and reducing reliance on imports, contributing to the technology sector's growth.